In the earliest economies, goods and services were exchanged directly, and that was practical only in small communities with simple needs.
As economies grew and trade expanded, the use of currency facilitated more complex transactions, including those between businesses.
With the establishment of banking systems, businesses began using checks to settle transactions, providing a safer and more practical method than carrying large amounts of cash.
The latter half of the 20th century saw the introduction of electronic payment methods, namely electronic funds transfer (EFT) and wire transfers, marking a significant shift towards digitalization.
The internet further revolutionized B2B payments, with online banking and payment platforms enabling faster and more secure transactions across borders.
Today, the latest evolution in this field involves the automation of payment processes and the rise of fintech companies offering specialized B2B payment solutions.
Automating B2B payments can offer numerous benefits to both buyers and suppliers. It streamlines the payment process, reduces errors and delays, and enhances visibility into cash flow.
In this guide, we will explore the steps involved in automating B2B payments and how this can benefit your business.
What Is B2B Payment Automation?
B2B payment automation refers to the process of using technology and software to streamline and simplify business-to-business payments. This often includes automating invoice processing, payment approvals, and reconciliation. Payment automation allows for faster, more accurate payments while minimizing manual efforts.
Some of the common features of B2B payment automation include:
- Integration with accounting and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems
- Electronic invoice presentment and payment (EIPP)
- Electronic data interchange (EDI)
- Automated clearing house (ACH) payments
- Virtual credit card payments
- Payment tracking and reporting capabilities
In essence, B2B payment automation represents a significant shift from manual, paper-based processes to more streamlined, efficient, and digital methods. It not only optimizes payment operations but also provides strategic advantages by improving cash management, enhancing relationships with business partners, and offering actionable financial insights.
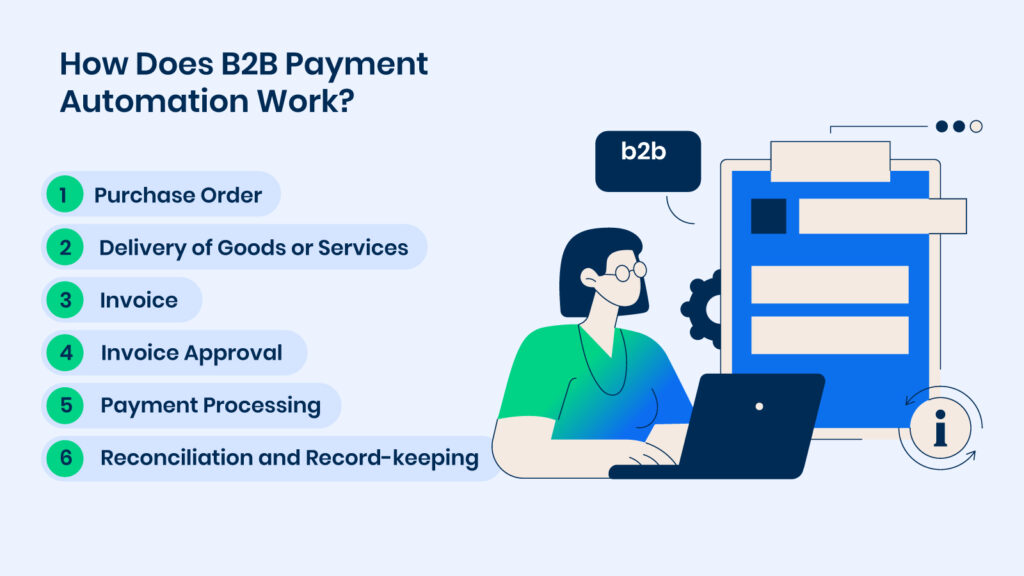
How Does B2B Payment Automation Work?
B2B payment automation streamlines transactions between two companies, which are typically more complex due to larger transaction volumes, higher values, and the intricacies of transactions that often involve credit terms, invoicing, and contractual agreements.
Here’s an overview of how B2B payments work:
1) Purchase Order
The process begins when a buyer needs goods or services from a supplier. The buyer creates a purchase order (PO) detailing the purchase, including quantities, descriptions, prices, and payment terms. This PO is sent to the supplier for approval. Once accepted, it becomes a legally binding contract.
2) Delivery of Goods or Services
The supplier delivers the goods or services according to the agreement. This may involve shipping physical products, providing digital goods, or completing a service.
3) Invoice
After delivery, the supplier issues an invoice based on the purchase order. This invoice outlines the provided products or services, the total due, and the payment terms. It is then sent to the buyer, often electronically via email or a B2B payment platform, though some still use postal mail.
4) Invoice Approval
The buyer verifies that the invoice matches the PO and the received goods/services. If all details align, the invoice is approved for payment. Any discrepancies must be resolved before proceeding.
5) Payment Processing
Upon invoice approval, the buyer processes the payment as per the agreed terms (for example, net 30 days). Payment methods include bank transfers, ACH, wire transfers, checks, or B2B payment platforms. The processing time varies by method.
6) Reconciliation and Record-keeping
Both parties update their records to reflect the transaction. The supplier marks the invoice as paid, and the buyer logs the payment as an expense. This step is essential for accurate financial reporting and tax compliance.
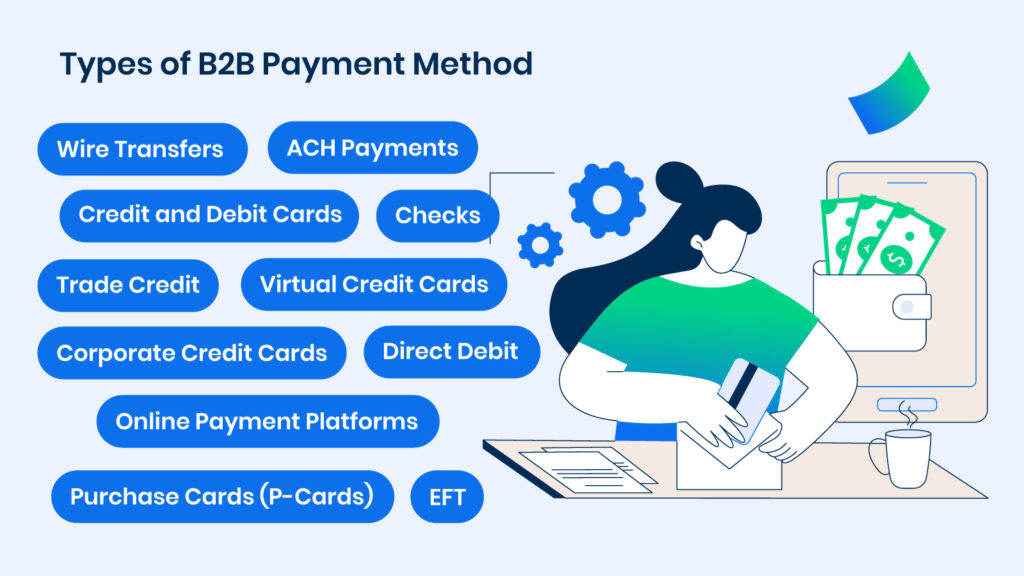
Types of B2B Payment Method
Wire Transfers
Wire transfers offer a swift and secure means for transferring funds directly between banks, making them a preferred option for high-value, time-sensitive transactions globally. Once initiated, wire transfer transactions are irreversible, providing a guarantee of payment to the recipient. The primary drawback is the higher transaction costs, especially for international payments, where additional fees and exchange rate considerations come into play.
ACH Payments
The Automated Clearing House (ACH) network supports electronic payments and money transfers across accounts, championing cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency. Especially suited for routine transactions like payroll, tax payments, and supplier payments, ACH transfers are more economical than wire transfers but have a longer processing time, typically clearing within 1-3 business days. This method balances cost savings against speed, favoring transactions where immediate settlement is not critical.
Checks
Despite the surge in electronic payment methods, traditional checks remain entrenched in certain sectors and regions, such as the U.S., for their simplicity and wide acceptance. Checks do not necessitate sharing sensitive bank information but are subject to longer processing times, mail delays, and an elevated risk of fraud and loss, making them less efficient and secure compared to digital alternatives.
Credit and Debit Cards
Credit and debit cards offer a convenient and immediate payment option for B2B transactions, ideal for lower-value purchases or when quick settlement is necessary. The broad acceptance of cards and the potential for rewards make them attractive, although they typically incur higher processing fees, which can accumulate significantly for large transactions.
Virtual Credit Cards
Virtual credit cards (VCCs) offer a digital version of traditional credit cards, with unique card numbers for each transaction. The limited lifespan and specific usage restrictions make them more secure against fraud and account takeover. VCCs are becoming increasingly popular in B2B payments due to their high level of security, automated tracking capabilities, and the potential for cashback rewards.
Corporate Credit Cards
Tailored for business usage, corporate credit cards facilitate higher spending limits and detailed reporting for expense management, along with rewards programs designed to meet corporate expenditure patterns. These cards necessitate diligent management to optimize benefits while avoiding pitfalls like high interest rates and fees.
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT)
Encompassing various types of electronic payments, including wire transfers and ACH payments, EFTs offer a secure and efficient means to move funds between accounts electronically. This broad category represents the shift towards digitization, aiming to enhance the speed and security of financial transactions while minimizing reliance on paper-based processes.
Digital Wallets and Mobile Payments
Digital wallets and mobile payment services, such as PayPal and Apple Pay, provide businesses with a fast, user-friendly platform for executing transactions. Particularly suited for smaller, on-the-go payments, these methods streamline the payment process, although their utility may be constrained by network acceptance and varying fee structures.
Online Payment Platforms
Services like Stripe and Square modernize B2B payments by supporting a multitude of payment methods through a single online platform. These platforms offer comprehensive solutions for managing invoices, billing, and payments, enriched with security features to safeguard transactions. They serve as a bridge between traditional banking services and the digital economy, catering to a broad spectrum of business needs.
Purchase Cards (P-Cards)
P-Cards are designed to streamline the procurement process by bypassing traditional purchase orders and invoice systems for low-value transactions, thus enabling efficient transaction management and detailed spending oversight. This method significantly reduces administrative costs and processing times, fostering operational efficiency.
Trade Credit
Trade credit is a vital mechanism within B2B transactions, allowing buyers to defer payment for goods and services. This practice enhances liquidity and operational flexibility for buyers while demanding effective credit management to mitigate financial risks. Maintaining a balance between extending credit and managing cash flow is crucial for sustaining healthy business operations and relationships.
Direct Debit
Direct debit facilitates automatic withdrawals from the buyer’s bank account, scheduled at regular intervals. This method is ideal for managing recurring payments, ensuring timely settlements without necessitating manual intervention. It enhances convenience and reliability in ongoing business engagements, such as subscriptions and service contracts.
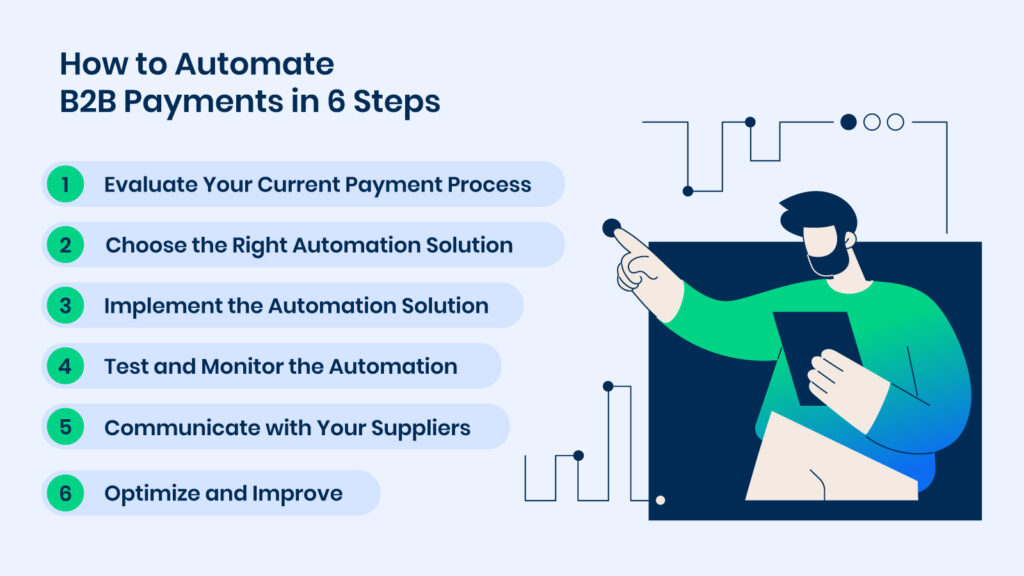
How to Automate B2B Payments in 6 Steps
Automating B2B payments is a strategic move that can significantly enhance operational efficiency, accuracy, and security in financial transactions. By transitioning from manual processes to automated ones, companies can streamline their payment workflows, reduce administrative overhead, and focus on core business activities. This automation not only saves time but also minimizes errors, improves cash flow management, and strengthens supplier relationships.
Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide to help you navigate the transition from manual to automated B2B payments:
Step 1: Evaluate Your Current Payment Process
The first step in automating your B2B payments is to evaluate your current process. Start by examining all the steps involved in making a payment, from creating invoices to sending and receiving payments. Identify any pain points or areas for improvement, such as manual data entry, delays in approvals, or lack of visibility into payment status. Understanding your current process is crucial for determining what needs automation.
Step 2: Choose the Right Automation Solution
After identifying areas that need improvement, select an automation solution that fits your business needs. Options range from standalone software to integrated platforms offering end-to-end payment automation. Consider factors like cost, features, and integration capabilities when making your selection.
Step 3: Implement the Automation Solution
With your chosen solution, integrate it into your existing systems. This may involve connecting with your accounting software or ERP system to streamline data transfer and minimize manual entry. Ensure you have a clear implementation plan and engage all stakeholders to facilitate a smooth transition.
Step 4: Test and Monitor the Automation
Before fully implementing your automation solution, conduct thorough testing to ensure its functionality and make any necessary adjustments. This should include testing data transfers, approval workflows, and payment processing. Continue to monitor the system post-implementation to identify any issues or areas for enhancement.
Step 5: Communicate with Your Suppliers
Effective communication with your suppliers is essential when implementing B2B payment automation. Inform them about the changes and how they will be impacted to prevent confusion or disruptions. Providing training or support for using the new system may also be necessary.
Step 6: Optimize and Improve
B2B payment automation is an ongoing process. Continue to monitor its performance and look for ways to further optimize and enhance the process. This may involve automating additional steps or adding new features as your business needs evolve. Regularly reviewing and improving your automation strategy will help keep your payments efficient, secure, and cost-effective.
The transition from manual to automated B2B payment processes marks a significant shift towards operational excellence. By following the outlined steps, your business can overcome the traditional challenges associated with B2B transactions. It is crucial to continually evaluate, implement, test, and optimize these automated systems to keep pace with evolving technologies. If you’re still uncertain about the necessity of this transition, let’s delve deeper into the benefits that B2B payment automation offers.
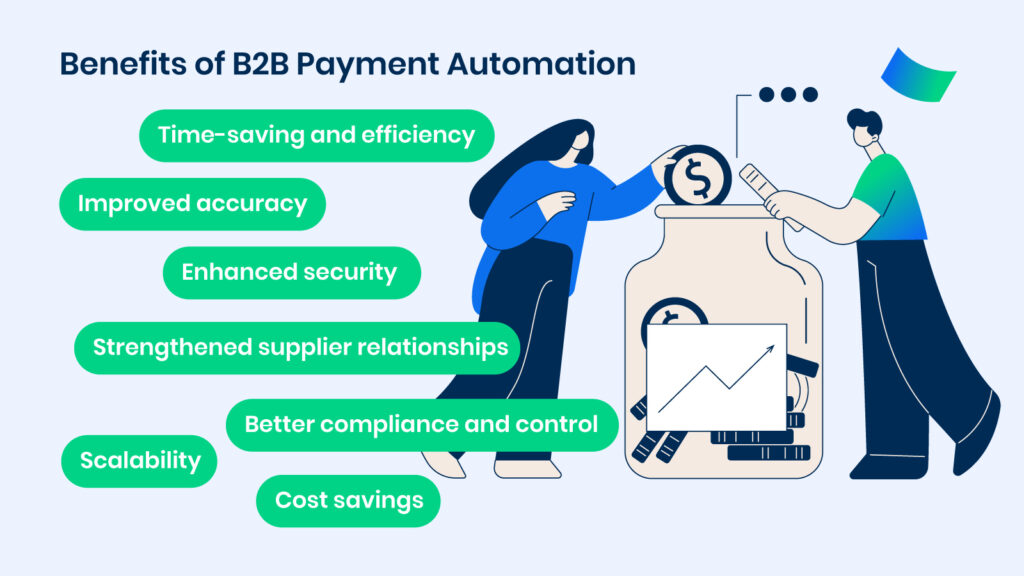
Benefits of B2B Payment Automation
B2B payment automation offers a suite of benefits that transform the financial operations of businesses, emphasizing efficiency, accuracy, and security. By automating the end-to-end payment process, from invoicing to reconciliation, companies can shift their focus from administrative tasks to strategic financial planning. The key benefits include:
- Time-saving and efficiency: Automation significantly reduces the time required for data entry, approvals, and processing. It eliminates manual tasks and streamlines operations, leading to a more efficient payment process and allowing employees to concentrate on higher-value activities.
- Improved accuracy: The reduction of human intervention in the payment process decreases the likelihood of errors in data entry and calculations, ensuring payments are processed correctly and financial records are accurately maintained.
- Enhanced security: With features like encryption and secure access controls, automated payment systems offer robust protection against fraud and unauthorized access, safeguarding sensitive financial data.
- Cost savings: By reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing errors that can lead to financial disputes or penalties, automation leads to considerable cost savings over time.
- Strengthened supplier relationships: Faster processing times and reliable payment schedules foster stronger relationships with suppliers, contributing to a more stable and efficient supply chain.
- Scalability: Automation solutions easily adapt to increased transaction volumes, supporting business growth without a proportional increase in administrative workload or costs.
- Better compliance and control: Automated systems provide an auditable trail of transactions and enforce compliance with financial regulations, ensuring all payments are authorized and properly recorded.
How DOKKA Can Help You Automate B2B Payments
DOKKA is a platform designed to automate various aspects of the bookkeeping and financial document management process, which can significantly streamline the B2B payment process. DOKKA can help automate B2B payments based on standard features of financial automation platforms:
- Document Capture and Management: DOKKA can automate the capture of financial documents, such as invoices and receipts, using AI technology. This process involves scanning, digitizing, and categorizing documents, making it easier to manage and retrieve them when needed. This foundational step ensures that all payment-related documents are in one place, accessible, and ready for processing.
- Invoice Processing: By automating invoice processing, DOKKA can extract relevant data from invoices using OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology. This reduces the need for manual data entry, minimizes errors, and speeds up the approval process. Automation can recognize due dates, amounts, and supplier details to streamline payments.
- Integration with Accounting Software: DOKKA likely integrates with popular accounting ERP platforms. This integration allows for seamless synchronization of financial data, enabling automated updates to your ledgers and accounts payable/receivable. As payments are processed, your accounting records are automatically updated, maintaining accurate financial statements.
- Automated Payment Approvals: DOKKA offers workflows that support automated payment approvals. By setting up predefined rules and conditions, payments can be automatically approved based on certain criteria, such as the amount, the supplier, or the payment due date, which accelerates the payment process and reduces bottlenecks.
- Payment Processing: While DOKKA itself may not process payments directly, it can facilitate the payment process by integrating with payment platforms. This integration can allow users to initiate payments directly from the platform, ensuring that payments are made promptly and recorded accurately in the accounting software.
- Audit Trail and Compliance: DOKKA provides a comprehensive audit trail of all transactions and document interactions. This is crucial for compliance purposes, ensuring that your business adheres to financial regulations and standards. It also simplifies the audit process by providing easy access to all necessary documentation and transaction histories.
- Supplier Communication: The platform may include features to communicate directly with suppliers, such as sending automated payment notifications or inquiries regarding invoices. This helps in maintaining good supplier relationships and ensuring that any discrepancies are quickly resolved.
To understand how DOKKA specifically can help automate your B2B payments, book a demo call with our support team for a demonstration and more detailed information about our offerings.








