Digital transformation has become a key priority for businesses across all industries. As companies strive to stay competitive and deliver better services, they are constantly looking for ways to streamline their processes and increase the efficiency of business operations.
But there is always the question: which processes should be improved and how?
One of the primary culprits that hinder business efficiency is the reliance on manual and complex processes. These outdated methods are not only time-consuming but also prone to errors, and they often inevitably lead to increased costs and reduced productivity.
The procure to pay (P2P) process is a perfect example of an area that often suffers from such inefficiencies. Why? Because P2P encompasses a range of activities from requisitioning goods and services to processing invoices and making payments. When handled manually, these activities can significantly slow down operations and create bottlenecks.
That is why the P2P process is one very important area that can greatly benefit from automation. This guide will provide an in-depth understanding of P2P automation and how it can transform your business.

What Is Procure to Pay (P2P) Automation?
Procure to pay (P2P) automation is the process of automating the entire procurement cycle, from purchase requisition to payment processing. It involves using technology and software solutions to streamline and digitize various stages of the procurement process, including vendor selection, purchase order creation, invoice processing, and payment execution.
In essence, P2P automation is designed to improve the efficiency and accuracy of the procurement process by eliminating manual tasks and introducing streamlined workflows. By automating P2P, companies can achieve faster cycle times, reduce errors and delays, increase visibility into spending, and ultimately save time and money.
Moreover, P2P automation improves supplier relationships by guaranteeing timely and accurate payments. It also provides extensive data analytics and reporting capabilities, enabling businesses to gain deeper insights into their procurement activities, identify trends, and make informed strategic decisions.
As the business environment becomes increasingly competitive, the need for efficient and transparent procurement processes has never been more critical. Implementing P2P automation not only drives operational excellence but also supports compliance with regulatory requirements by maintaining accurate records and audit trails.
How Does P2P Automation Work?
The procure to pay (P2P) process starts with identifying a need for a product or service and ends with making the payment for it. Key steps involved in this process include sourcing, supplier selection, purchase order creation, receiving goods or services, invoicing, and payment processing.
Here is a detailed breakdown of how P2P automation works:
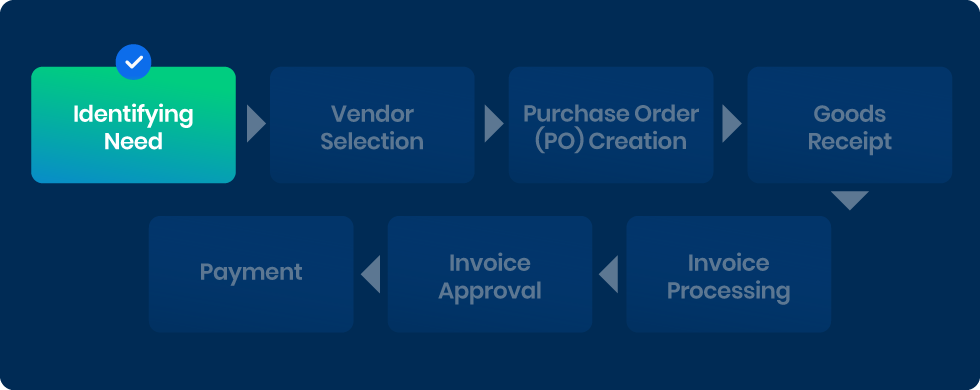
1) Identifying Need
The P2P automation process begins with identifying a need for a product or service within the organization. This need can be initiated by various departments such as procurement, operations, or finance.
Automation tools facilitate this step by allowing users to input requirements into a centralized system. This centralization ensures that all requisitions are captured accurately and that there is a clear, documented record of what is needed.
Once the need is logged, the system triggers the procurement workflow, notifying relevant stakeholders and setting the process in motion. This step is crucial as it lays the foundation for the entire procurement cycle, ensuring that all subsequent steps are aligned with the organization’s requirements.
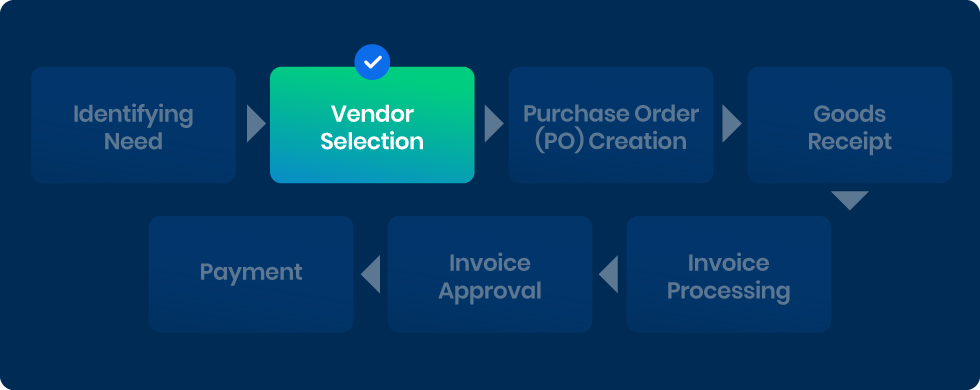
2) Vendor Selection
After identifying the need, the next step involves selecting the appropriate vendor or supplier. Automated P2P systems often include vendor management modules that store comprehensive profiles of potential suppliers. These profiles may contain information such as pricing, quality ratings, delivery performance, and historical transaction data.
The system can automatically assess vendors based on predefined criteria such as price, quality, delivery time, and vendor reputation. This automated assessment helps in making informed decisions by providing a comparative analysis of vendors, ensuring that the selected supplier meets the organization’s standards and requirements.
Additionally, automated systems can manage requests for proposals (RFPs) and requests for quotes (RFQs), streamlining the vendor selection process and ensuring transparency and fairness in supplier evaluations.
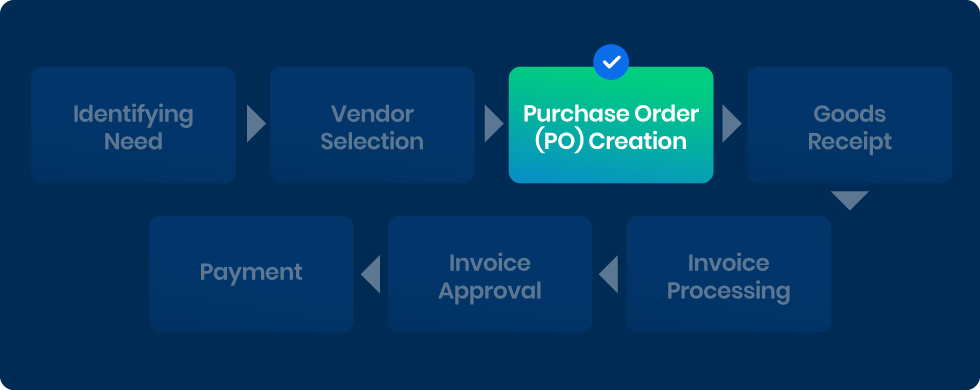
3) Purchase Order Creation
Once a vendor is selected, a purchase requisition is created, detailing the required goods or services, quantity, quality specifications, and any other relevant information. This requisition moves through an automated approval workflow, ensuring that all necessary approvals are obtained swiftly.
The automation system can be configured to route the requisition to the appropriate approvers based on the organization’s hierarchy and policies. Once approved, a purchase order (PO) is automatically generated and sent to the chosen vendor.
The PO includes specific details such as item descriptions, quantities, prices, delivery dates, and terms and conditions. This automated generation of POs ensures accuracy and consistency, reducing the risk of errors that can occur with manual order creation.
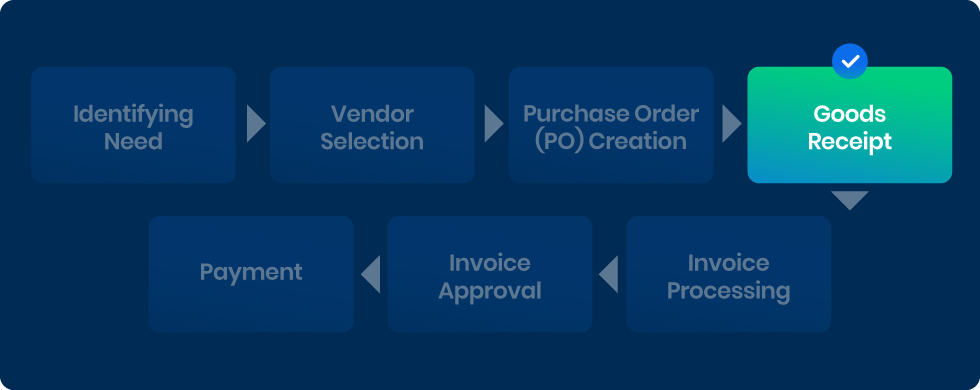
4) Goods Receipt
The vendor acknowledges receipt of the PO and confirms the order details, typically by sending an order confirmation or acceptance.
Upon receiving the goods or services, the receiving department uses the automated system to compare them with the details specified in the PO. They check for quality, quantity, and any discrepancies. An automated system can use barcodes or RFID technology to facilitate this comparison, ensuring that the received items match the ordered specifications. If there are any discrepancies, the system can trigger alerts and initiate corrective actions.
A goods receipt note (GRN) is created within the system to confirm receipt, documenting that the goods or services have been received as per the order. This automated step ensures accountability and traceability in the receipt of goods.
5) Invoice Processing
Following the delivery, the vendor sends an invoice for the goods or services provided.
The P2P system automatically matches the invoice against the PO and GRN to ensure accuracy in terms of quantity, price, and other terms. This three-way matching process is critical in identifying and rectifying discrepancies promptly, preventing overpayments or underpayments.
Automated invoice processing significantly reduces the time and effort required to verify invoices, enabling faster and more accurate financial reconciliation. If discrepancies are found, the system can flag these issues and send them for resolution before payment is processed, ensuring that only valid invoices are paid.
6) Invoice Approval
The invoice undergoes an automated approval workflow within the organization based on predefined rules and roles. This may involve verification by the receiving department, budget owner, and finance team.
Automation ensures that the approval process is swift and compliant with internal policies. The system routes the invoice through the necessary approvals, tracking the status at each stage and providing notifications to approvers.
This automated workflow reduces bottlenecks and ensures that invoices are approved in a timely manner, preventing delays in payment processing and improving the organization’s cash flow management.
7) Payment Processing
Once the invoice is approved, the automated system schedules and processes payment according to the agreed-upon payment terms, such as net 30 days.
Payment can be made through various methods such as electronic funds transfer (EFT), checks, or other electronic payment systems.
The system also records the transaction and updates the financial records automatically. This ensures that payments are made accurately and on time, maintaining good relationships with suppliers and avoiding late payment penalties.
Automated payment processing also provides detailed audit trails and reporting capabilities, enhancing financial transparency and accountability within the organization.
Why You Should Automate Procure to Pay (P2P) Process?
Automating the P2P process revolutionizes how organizations manage their procurement and payment workflows.
Traditionally, P2P has been handled manually, involving paper-based systems that are prone to errors, delays, and lack of transparency. These inefficiencies significantly impact organizational productivity and financial performance.
Errors in purchase orders, invoices, and payment reconciliations often lead to overpayments, late fees, and strained supplier relationships. Moreover, manual processes consume valuable human resources, tying up employees in repetitive tasks that could be better utilized for strategic initiatives.
Automation of the P2P process addresses these challenges by leveraging technology to streamline operations. Automated systems ensure accuracy by electronically matching purchase orders with invoices and facilitating prompt payment processing. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances compliance with procurement policies and regulatory requirements.
Real-time visibility into procurement activities and financial data enables organizations to make informed decisions, optimize spending, and strategize effectively for future growth.
Furthermore, P2P automation seamlessly integrates with other enterprise systems such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms. This integration creates a cohesive business ecosystem where data flows seamlessly across departments, enhancing overall operational efficiency and supporting scalability in a dynamic market environment.

Key Benefits of Automating Procure to Pay (P2P)
Automating the P2P process offers significant advantages that enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve strategic decision-making capabilities for organizations.
Here are the key benefits of implementing P2P automation:
- Improved Efficiency
- Cost Savings
- Enhanced Accuracy and Compliance
- Faster Cycle Times
- Improved Supplier Relationships
- Enhanced Visibility and Reporting
- Scalability and Flexibility
Improved Efficiency
P2P automation reduces manual intervention across various stages of the procurement cycle. By automating these processes, organizations experience faster processing times and fewer errors, ultimately boosting overall efficiency. Tasks that once required extensive human effort can now be completed swiftly and accurately, enabling employees to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Cost Savings
Automation of P2P processes leads to substantial cost savings by eliminating expenses associated with manual handling, such as labor costs, paper-based documentation, and processing errors. Organizations can also identify cost-saving opportunities through enhanced visibility into spending patterns and supplier relationships. By streamlining procurement operations, automation reduces operational costs and optimizes resource allocation, contributing directly to improved financial performance.
Enhanced Accuracy and Compliance
Automated P2P systems ensure greater accuracy in data entry and transaction processing. By applying consistent approval workflows and controls throughout the procurement cycle, automation helps enforce compliance with internal policies and external regulations. This reduces the risk of errors and ensures that all transactions meet regulatory requirements, enhancing overall financial accuracy and compliance.
Faster Cycle Times
Automation significantly reduces cycle times from requisition to payment, accelerating the entire procurement process. This speed is crucial for meeting operational needs promptly and improving responsiveness to market demands. Shorter cycle times enable organizations to capitalize on opportunities quickly and maintain competitive agility in dynamic business environments.
Improved Supplier Relationships
P2P automation facilitates smoother communication and collaboration with suppliers. By automating interactions from order placement to invoice processing, organizations can enhance transparency and efficiency in supplier relationships. Quicker issue resolution and timely payments improve supplier satisfaction and foster long-term partnerships based on trust and mutual benefit.
Enhanced Visibility and Reporting
Automated P2P systems provide real-time visibility into spending and procurement activities. This transparency allows organizations to make informed decisions, identify trends, and optimize purchasing strategies based on accurate data and analytics. Detailed reporting capabilities enable stakeholders to monitor performance metrics, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and drive continuous improvement across the procurement function.
Scalability and Flexibility
Automation supports scalability as organizations grow or experience fluctuations in demand. Automated systems adapt seamlessly to varying transaction volumes and business needs without compromising efficiency or accuracy. This scalability ensures that procurement operations can scale with business growth and effectively support organizational objectives without operational bottlenecks.








