Before you start reading this text, ask yourself:
“How much financial data do I need to process each month, each week, or at a single time?”
And the next question:
“How much of that data is outdated?”
Traditional accounting methods, grounded in reactive and historical processes, are being reshaped by a forward-thinking model that emphasizes real-time data analysis and decision-making.
Continuous accounting is a transformative approach redefining the way modern finance teams operate. Shifting away from periodic, end-of-cycle tasks, continuous accounting empowers organizations to leverage real-time financial intelligence.
Rather than discarding traditional accounting principles, this model builds upon them through the strategic integration of technology and automation.
As processing speeds increase and real-time insights become more accessible, manual tasks are reduced, enabling finance teams to operate with greater accuracy, efficiency, and agility.
And that’s only the beginning. In the sections ahead, we’ll explore the core principles of continuous accounting, examine why it’s rapidly becoming the gold standard in modern finance, and outline the compelling benefits this shift can bring to your business.

What is Continuous Accounting?
Continuous accounting is a modern approach to managing financial records and processes that integrates the recording, processing, and analyzing of financial data continuously throughout an accounting period.
It stands in contrast to the traditional batch processing method, where financial activities are compiled, processed, and reported at fixed intervals, typically at the end of a month, quarter, or year.
Continuous accounting eliminates the traditional periods or ‘close windows’ that require tedious manual labor. Instead, it enables finance teams to continuously update their records and generate accurate financial statements and reports in real-time.
The Tech Behind Continuous Accounting
With the abundance of financial data generated by businesses, traditional manual processes are no longer sufficient to keep pace with the complexity of modern finance operations.
Technology offers a solution through the automation of many time-consuming tasks, enabling finance teams to focus on higher-value analytical work.
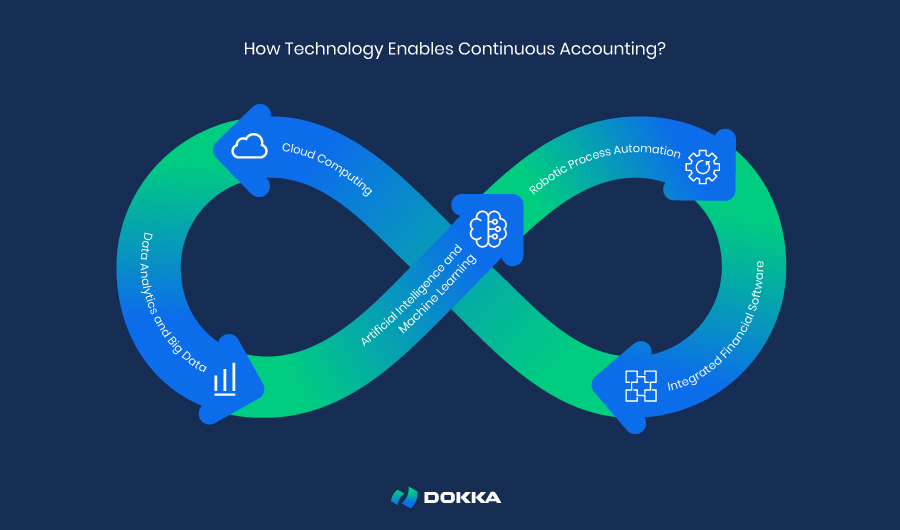
Key technologies driving continuous accounting include:
- Cloud Computing: Provides secure, scalable, and accessible storage and processing of vast amounts of financial data from a centralized location or hub. It supports real-time data analysis and collaboration among finance teams, regardless of geographical location.
- Data Analytics and Big Data: Enables the examination of large datasets to extract meaningful insights and trends, including predictive analytics, anomaly detection, and fraud detection.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are transforming how financial data is collected, analyzed, and reported. Intelligent algorithms can process large volumes of data in real-time, detect patterns and anomalies, and produce accurate reports significantly faster than manual methods.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Plays a critical role in continuous accounting by automating repetitive, manual tasks. RPA boosts efficiency, minimizes errors, and frees up resources for more strategic and analytical activities.
- Integrated Accounting Software: Modern solutions integrate Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems with purpose-built accounting platforms to provide a unified environment for managing financial processes.
Together, these technological advancements have made continuous accounting a practical reality. Automation empowers finance teams to operate with greater agility and precision, transforming financial management into a more strategic, efficient, and forward-looking discipline.
8 Key Benefits of Continuous Accounting
Continuous accounting is rapidly emerging as the preferred approach to modern finance, and for good reason. Its benefits extend well beyond accelerating the financial close, transforming the finance function to deliver greater accuracy, agility, and strategic impact.
Here are 8 key advantages driving the shift toward continuous accounting as the new standard:
- Real-Time Financial Insight
- Improved Accuracy
- Increased Efficiency
- Stronger Compliance
- Smarter Decision-Making
- Higher Employee Satisfaction
- Greater Stakeholder Confidence
- Scalable Growth
1) Real-Time Financial Insight
Traditional accounting often trails actual business activity, but continuous accounting offers real-time visibility into financial performance. This immediacy enables leaders to make faster, better-informed decisions.
2) Improved Accuracy
Routine and repetitive tasks are automated, significantly reducing the potential for human error. Automated entries help maintain consistent, high-quality data and strengthen the reliability of financial reporting.
3) Increased Efficiency
Month-end and year-end closes are streamlined, cutting down on time and manual effort. As a result, finance teams can focus more on strategic tasks such as analysis and forecasting.
4) Stronger Compliance
Maintaining consistent, automated records simplifies adherence to regulatory standards. Clear documentation and improved transparency make it easier to meet evolving compliance and audit requirements.
5) Smarter Decision-Making
A continuous flow of current financial data supports agile planning. Businesses can adapt quickly to market changes and align strategies with up-to-date performance indicators.
6) Higher Employee Satisfaction
Reducing last-minute crunches and repetitive work helps lower stress levels. Finance professionals gain more time to contribute to meaningful projects that drive business value.
7) Greater Stakeholder Confidence
Reliable, timely reporting strengthens trust among investors, lenders, and other stakeholders. Continuous accounting promotes transparency by ensuring access to accurate, real-time financial data.
8) Scalable Growth
As organizations grow, continuous accounting easily scales to accommodate increased transaction volume. Its automated structure eliminates the need for proportional increases in staffing or manual intervention.

How To Get Started With Continuous Accounting
Implementing continuous accounting in a company is a transformative process that requires strategic planning and a methodical approach.
The complexity of the transition can easily lead to confusion, so it’s important to start with clear, actionable steps:
- Identify Key Processes
- Invest in Technology
- Redesign Processes
- Train Employees
- Monitor and Evaluate
- Identify Key Processes
Begin by identifying which accounting tasks stand to gain the most from automation.
Routine activities such as journal entries, reconciliations, and intercompany transactions often consume significant time and are prone to human error.
Evaluate your current accounting workflow to uncover inefficiencies and determine which processes are best suited for streamlining.
Prioritize automation based on potential efficiency gains and ease of implementation.
- Invest in Technology
Effective continuous accounting depends on robust technology.
Investing in automation tools and cloud-based software tailored to your organization’s needs is essential.
Ensure the chosen technology integrates smoothly with existing systems to maintain consistent data flow and minimize disruption.
Scalability should also be a key consideration to support future growth.
- Redesign Processes
Shifting from periodic reporting to continuous accounting requires a fundamental redesign of traditional accounting processes.
Introducing automated workflows helps reduce manual labor and increases accuracy across tasks such as data entry, transaction matching, and report generation.
Real-time reporting also necessitates changes in how data is collected and analyzed, enabling faster, more informed decision-making.
- Train Employees
Equipping your team with the necessary skills is critical to the success of the transition.
Develop training programs that address both the new technology and the core concepts of continuous accounting. Offer ongoing learning opportunities to keep employees up to date with evolving tools and practices.
Cultivating an adaptive mindset within your team will help ensure long-term adoption and effectiveness.
- Monitor and Evaluate
Define clear metrics to measure the effectiveness of your continuous accounting implementation.
Regularly review performance against these benchmarks, and remain open to refining your approach based on feedback and outcomes.
Continuous accounting is inherently iterative, requiring ongoing improvements to meet changing business needs.
Continuous Accounting FAQ
How is continuous accounting different from traditional accounting?
Traditional accounting focuses on month-end or quarter-end tasks, while continuous accounting spreads tasks throughout the period. This approach creates balanced workloads, faster closes, and real-time insights.
Traditional accounting operates primarily at the end of the period, whereas continuous accounting functions daily.
Traditional methods rely on past data, but continuous accounting uses real-time data. Traditional accounting often depends on manual processes, while continuous accounting leverages automation and integration.
For risk management, traditional accounting addresses issues after the close, while continuous accounting enables continuous monitoring and earlier issue detection.
What are the core goals of continuous accounting?
- Accelerate financial close
- Increase accuracy and compliance
- Provide real-time visibility into performance
- Enable strategic decision-making through timely data
What tools are needed to implement continuous accounting?
Common tools include ERP systems, RPA platforms, reconciliation tools, analytics dashboards, and workflow automation tools.
Can continuous accounting be implemented gradually?
Yes. Many organizations start by automating high-volume tasks like bank reconciliations or journal entries, then expand into more complex areas such as intercompany eliminations, revenue recognition, and forecasting.
How long does implementation typically take?
Implementation time depends on company size and readiness. A small-scale rollout can take 3–6 months; a full transformation for large enterprises may take 12–24 months.
What processes can be automated first?
- Bank reconciliations
- Journal entries
- Intercompany transactions
- Accounts payable and receivable matching
- Accrual entries
- Expense categorizations
Is continuous accounting audit-friendly?
Yes. Continuous accounting often improves audit readiness by maintaining real-time, traceable records and consistent controls. Many automation software solutions include built-in audit trails.








