It’s 2025 and it seems that many companies are still not aware that automating accounts payable is a complete game changer.
The traditional AP process is manual, time-consuming, very prone to human error, and often results in delays and financial discrepancies. We are on a mission to flip that around.
Today’s post will explore the benefits of automating your accounts payable (AP) processes, clarify common use cases for automation, and offer a step-by-step guide for transitioning from manual to automated systems.
![]()
Manual vs Automated AP
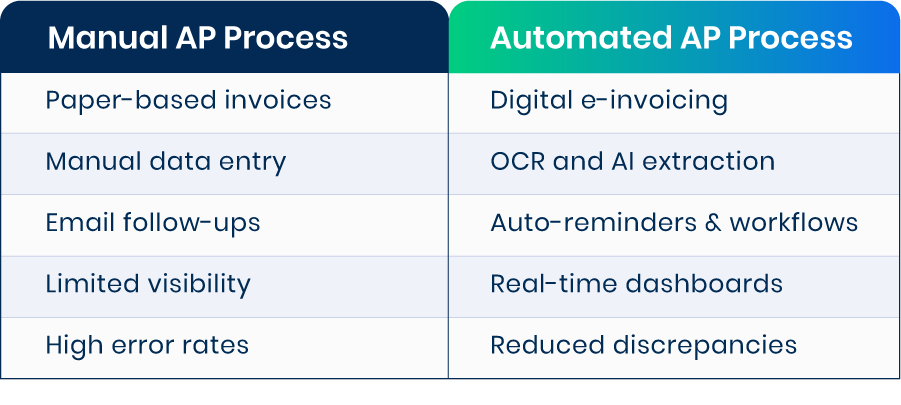
Traditionally, managing AP has been a labor-intensive process. It involves receiving and reviewing invoices, matching them against purchase orders (POs) and contracts, entering data into accounting systems, securing internal approvals, and issuing payments.
Manual workflows often lead to issues such as duplicate payments, incorrect data entry, and misplaced invoices. Over time, these inefficiencies can cause payment delays and strain relationships with suppliers.
Effective AP management is essential for maintaining healthy cash flow and vendor trust.
Automating AP processes offers a range of benefits, including:
- Lower invoice processing costs
- Increased accuracy
- Greater operational efficiency
- Improved compliance with regulatory standards
Automation reduces the time and resources required for repetitive tasks like data entry and invoice handling. It also enables companies to scale more efficiently, without AP becoming a bottleneck to growth.
![]()
How to Automate Accounts Payable: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Review Current AP Workflow
- Select an Automation Platform
- Automate Invoice Capture
- Set Up Approval Workflows
- Launch Vendor Portal
- Train Users and Build Support
- Monitor and Optimize
![]()
Step 1: Audit and Analyze Your Current AP Workflow
- Start by thoroughly reviewing your existing accounts payable process—from invoice receipt through to final payment. Map out each step to uncover manual tasks, delays, frequent errors, and inefficiencies in approvals.
- Collect feedback from finance personnel, department managers, and approvers to identify the root causes of issues such as lost invoices, late payments, or compliance concerns.
- Use the findings from this analysis as a foundation for building an automation strategy tailored to your organization’s specific needs.
![]()
Step 2: Choose an AP Automation Solution That Aligns with Your Infrastructure
- Select a platform that integrates seamlessly with your existing ERP or accounting software (e.g., DOKKA, Stampli or Tipalti).
- Ensure the solution includes key features like intelligent invoice capture (OCR and e-invoicing), automated matching, approval routing, audit trails, and mobile accessibility.
- Scalability, ease of use, and minimal implementation overhead should be prioritized so the solution fits both current requirements and future growth.
![]()
Step 3: Streamline Invoice Capture and Digitization
- Remove the need for manual data entry by implementing automated invoice ingestion. Leverage OCR technology to extract data from paper or scanned invoices, and encourage vendors to send structured digital files.
- Digital invoice capture accelerates processing, minimizes human error, and guarantees secure, searchable storage. Laying this foundation also enables automatic PO matching and helps prevent duplicate entries.
![]()
Step 4: Configure Automated Workflows for Approval and Exception Handling
- Create workflows that mirror your internal controls and approval hierarchies. Set routing rules based on factors like invoice type, amount, vendor, or department.
- Incorporate role-based approvals, thresholds, and escalation paths to eliminate bottlenecks.
- Well-designed workflows reduce cycle times, limit manual intervention, and help ensure policy compliance throughout the process.
![]()
Step 5: Enable Vendor Collaboration Through Self-Service Portals
- Deploy a vendor portal that allows suppliers to upload invoices, monitor payment status, and update their own information.
- Offering this self-service option enhances transparency and cuts down on email and phone inquiries.
- Maintaining cleaner, up-to-date vendor data also helps reduce payment delays and processing errors.
![]()
Step 6: Train Stakeholders and Build Support for the New System
- Deliver targeted training to AP staff, approvers, and department users. Demonstrate the system using real invoice scenarios to highlight its practical benefits.
- Identify champions or early adopters who can promote usage and assist colleagues.
- Ongoing communication and feedback loops are essential for addressing concerns and continuously refining workflows after rollout.
![]()
Step 7: Monitor Performance and Optimize Over Time
- After implementation, track key performance indicators such as invoice cycle time, approval duration, and exception rates.
- Use built-in analytics or external reporting tools to evaluate effectiveness and identify areas for further automation.
- Refine workflows, adjust rules, and expand features based on insights gained from ongoing performance monitoring.
![]()
Top Use Cases of Accounts Payable Automation in 2025
- Electronic Invoicing
- Automated Invoice Processing
- Digital Approval Workflows
- Vendor Self-Service Portals
- Automated Payment Scheduling
- Integration with Accounting Software
- Machine Learning for Invoice Matching
- Document Management Systems
- Mobile Accessibility
- Data Analytics for AP Optimization
![]()
Electronic Invoicing

Electronic invoicing, or e-invoicing, replaces traditional paper invoices with digital versions, streamlining the entire AP workflow. It reduces the need for manual data entry, helping prevent errors and speeding up invoice processing.
Digital invoices can be automatically imported, stored, and matched with purchase orders, which makes tracking and audits more efficient.
Centralized and searchable document storage improves organization. In addition, e-invoicing supports sustainability through reduced paper usage and physical storage requirements.
![]()
Automated Invoice Processing

Automated invoice processing uses technologies such as OCR and machine learning to capture and process invoice data without manual input.
When an invoice arrives—via email or portal—the software extracts key details like dates, amounts, and vendor names. These details are automatically checked against POs and delivery receipts, with discrepancies flagged for review.
Invoices follow pre-defined workflow rules for routing and approval, and once approved, are synced with the accounting system. Speed, accuracy, and scalability are significantly improved.
![]()
Digital Approval Workflows

Digital approval workflows remove delays and confusion from manual approval processes. Invoices are routed through a structured path based on criteria like invoice value, vendor, or department.
Approvers receive real-time notifications and can review and sign off from any device, even when away from the office.
A full audit trail is maintained, recording who approved each item and when, which simplifies compliance. Faster approvals, fewer bottlenecks, and improved spending control are key outcomes.
![]()
Vendor Self-Service Portals

Vendor portals provide suppliers with real-time access to invoice and payment status, reducing the need for emails or phone calls.
AP automation makes vendor management easy – suppliers can upload invoices, track payment timelines, and update contact or banking information as needed.
This self-service model enhances transparency and builds trust with vendors. It also eases the AP team’s workload by minimizing routine inquiries. Keeping vendor information up to date helps prevent payment delays and reduce errors.
![]()
Automated Payment Scheduling

Automated payment scheduling ensures timely invoice payments by aligning with due dates and cash flow priorities.
The software identifies payment deadlines and sets up transactions accordingly, which helps avoid late fees and maintain strong supplier relationships.
Strategic payment planning supports optimized cash flow. Integration with accounting systems keeps financial data current and accurate. With fewer manual tasks, finance teams can dedicate more time to strategic activities.
![]()
Integration with Accounting Software

Integrating AP automation with accounting or ERP systems enables seamless data flow across departments.
Invoices processed in AP software are automatically reflected in the general ledger, maintaining accurate financial records. This reduces duplicate data entry, minimizes human error, and shortens month-end closing cycles.
Visibility into expenses is improved, and financial reporting remains consistent. The integration enhances audit readiness and overall operational efficiency.
![]()
Machine Learning for Invoice Matching

Machine learning improves invoice matching by learning from historical data to identify patterns and accommodate variations. It automatically matches invoices with purchase orders and goods receipts, even when there are common discrepancies such as rounding or delivery tolerances.
As the system continues to learn, accuracy improves and manual review becomes less necessary. Unusual entries or potential fraud can also be flagged for investigation, strengthening both accuracy and internal controls.
![]()
Document Management Systems

A Document Management System digitizes and organizes AP-related documents—including invoices, POs, and contracts—in one central location. Documents can be quickly searched and retrieved based on vendor, date, or invoice number.
OCR technology extracts text from scanned files, making them searchable. This facilitates audits, compliance, and internal reviews by ensuring easy access and traceability. Many DMS platforms also offer access controls and encryption to protect sensitive information.
![]()
Mobile Accessibility

Mobile access allows users to handle AP tasks from anywhere, at any time.
Approvers can review, comment on, and approve invoices directly from smartphones or tablets, maintaining workflow momentum even when away from the office. Real-time notifications reduce delays by prompting timely action.
Mobile apps also enable users to upload documents and receipts directly into the system. Security features, such as multi-factor authentication, help ensure safe mobile access to financial data.
![]()
Data Analytics for AP Optimization

Data analytics transforms accounts payable into a strategic function by revealing trends and opportunities for improvement.
Organizations can analyze spending habits, monitor processing times, and pinpoint bottlenecks or delays. Analytics tools support fraud detection by highlighting irregular transactions or vendor behavior.
Real-time AP data contributes to more accurate cash flow forecasting. Greater visibility into financial operations empowers teams to make smarter, faster decisions.
![]()
Automate Your Accounts Payable With DOKKA
DOKKA streamlines and simplifies accounts payable process, making it faster and more efficient.
Our platform integrates smoothly with your existing accounting system, and our streamlined onboarding process gets your team up and running quickly—no lengthy delays or complex setups. Experience immediate improvements in invoice processing, accuracy, and control.
Ready to transform your AP workflow? Book a demo today and see how DOKKA can simplify your accounts payable automation.